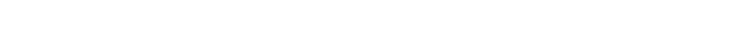SEO and UX are both essential in shaping a successful website.
While SEO boosts a site’s visibility in search results, UX ensures that visitors find the experience engaging and intuitive, keeping them on the site longer. These two areas work hand-in-hand, creating a space that’s both appealing to users and visible on search engines like Google.
The recent antitrust case against Google brought this connection into sharper focus. The case revealed that Google’s search rankings are influenced by user behavior, showing that UX plays a direct role in SEO. When a website is easy to navigate, loads quickly, and offers valuable content, users stay longer and engage more—key behaviors that Google uses to determine rankings. In other words, positive user experiences can now help improve search rankings.
In August 2024, the U.S. Department of Justice found that Google violated antitrust laws by maintaining a monopoly in search and advertising. This trial also exposed Google’s financial agreements with companies like Apple to remain the default search engine on devices, a move the DOJ argues limits competition. With fewer search engine choices, competitors have faced challenges in reaching users.
This case highlights why UX is now more than just good design. Sites that focus on speed, clarity, and relevant content attract more engaged users, which, in turn, can help with rankings. As a result, building websites that truly serve user needs is becoming a central part of SEO for businesses aiming to succeed on Google.
Core UX Elements That Affect SEO
User experience covers several elements that now directly impact Google rankings.
These key factors make a website more engaging for users and also help it rank higher on search engines:
- Page Speed and Performance
Fast-loading sites keep users engaged, while slow-loading pages often drive visitors away. Google considers page speed a ranking factor, so it’s crucial to ensure your pages load quickly. Compressing images, reducing unnecessary scripts, and using a content delivery network (CDN) are common ways to boost speed and keep users from bouncing. - Mobile Friendliness
Google evaluates a site’s mobile experience as part of its ranking system. A mobile-friendly website that adapts to different screen sizes and is easy to navigate can improve both user engagement and search visibility. Make sure buttons and links are easy to tap, and that navigation is clear and intuitive. - Navigation and Site Structure
Clear, logical navigation helps users find information quickly and boosts engagement. Google’s algorithms also reward sites with good structure, so keep page depth shallow, use simple menus, and include breadcrumb navigation. - Content Relevance and Quality
Google ranks pages based on the relevance and quality of their content. Engaging, informative content keeps users on the page longer, signaling value to Google. Ensure your content aligns with what users are looking for and addresses their questions directly. - Core Web Vitals
Google’s Core Web Vitals measure page load speed, interactivity, and visual stability. Metrics like Largest Contentful Paint (LCP) and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS) focus on how quickly content loads and how stable the layout is as it loads. Good scores in these areas improve user satisfaction and support higher rankings.
Google’s Ranking Systems and the Influence of User Data
Insights from recent trials have revealed that Google’s ranking algorithms prioritize search results based on user data, providing a closer look at how interaction data shapes the rankings we see:
RankBrain and DeepRank These machine-learning systems track how users interact with web pages to better understand search intent and content relevance. By studying patterns like clicks, time spent on a page, and overall engagement, these algorithms elevate pages that meet users’ needs.

Navboost and Glue These tools focus on behavior across search results. Navboost evaluates over a year’s worth of click data to pinpoint the most engaging results, while Glue assesses a range of interactions within search features. Pages with high engagement tend to rise in rankings, showing the link between user experience and search visibility.
Core Web Vitals This set of metrics gauges a site’s speed, interactivity, and stability. Pages that load quickly and remain stable provide a better experience, which positively affects their ranking.
How Google Uses Click Data to Refine Search Results
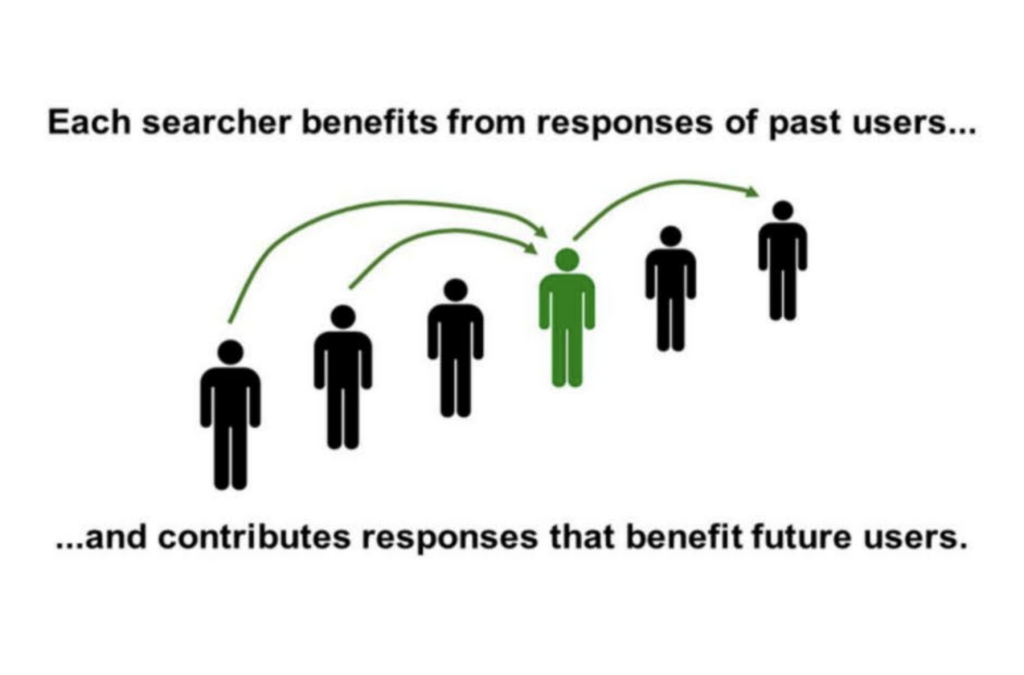
When you search on Google, your clicks contribute to a constantly improving system.
Each click, whether it’s a quick tap or a longer visit, helps Google learn which results are useful. Google tracks the links you choose, how long you stay, if you scroll, and whether you return to try another result. Each action feeds into a large pool of data that Google analyzes to improve future searches.
For instance, if a user searches for “best laptops for students” and clicks the top result but quickly returns to the search results to try another link, it indicates the first page might not have provided the desired information. If many users repeat this pattern, Google notices and adjusts the rankings, possibly lowering that page and favoring others that keep users engaged longer.
Conversely, when a user clicks on a link, explores the page, and doesn’t bounce back to Google immediately, it signals that the content was likely helpful. Pages that consistently hold users’ attention gain an advantage in ranking, as Google sees them as relevant and valuable.
Understanding User Interaction Signals
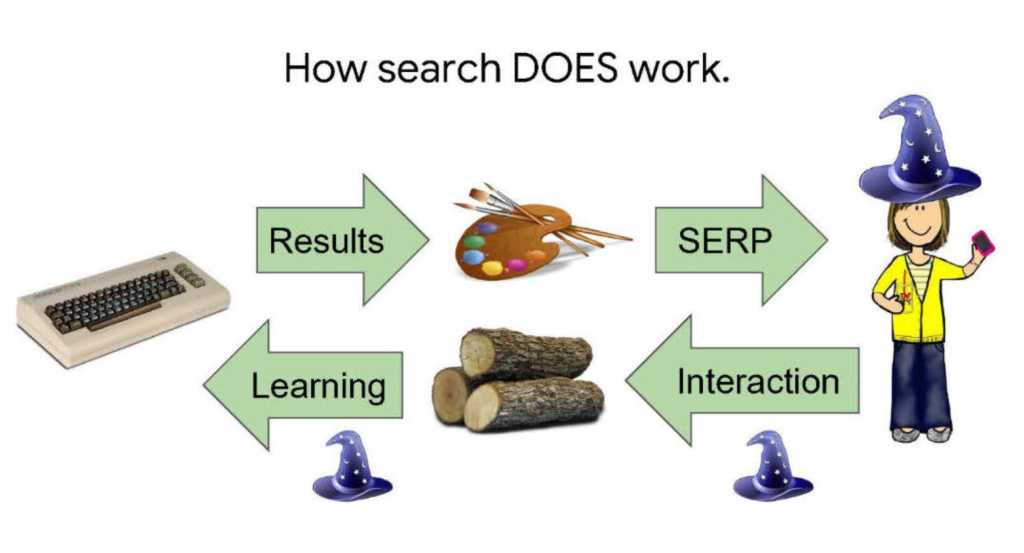
Click data is just one piece of the puzzle.
Google also monitors other interaction signals, like scrolling, hovering, and whether users stick to one result or explore multiple links. These actions help Google understand which parts of a page engage users and which content best answers their questions.
For example, if users scroll down to a particular section and spend time there, it’s a sign that this part of the page contains useful information.
Although these signals may seem minor, they play a significant role in shaping Google’s understanding of a page’s value. Over time, these signals influence Google’s algorithms, refining the search results to better align with what users want.
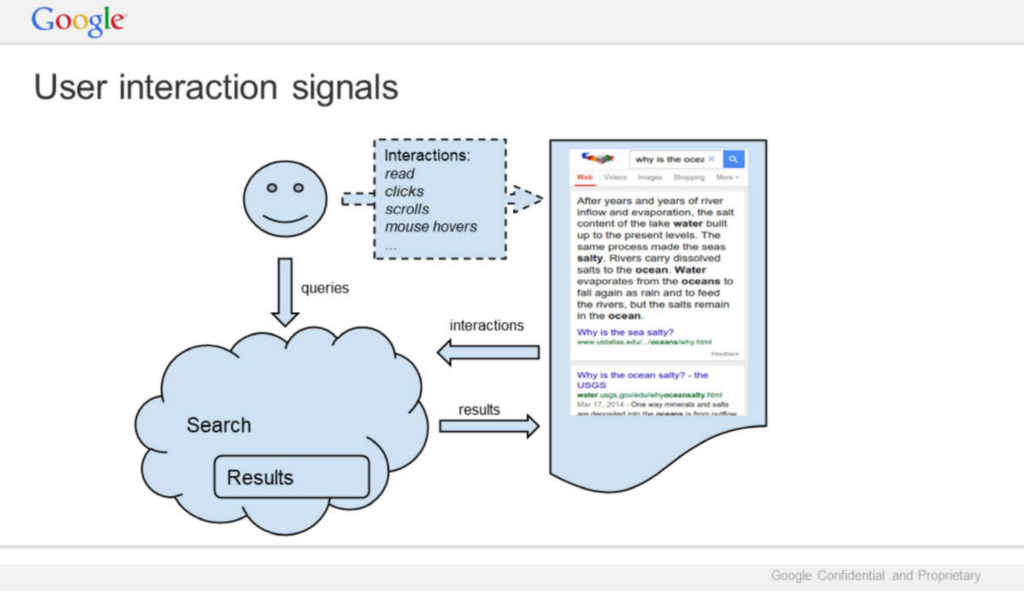
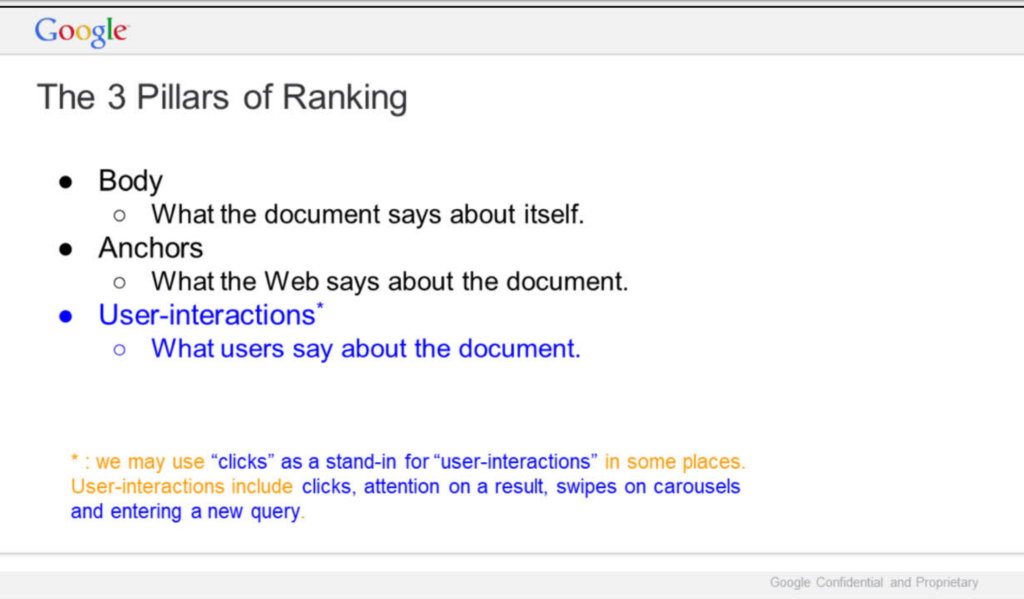
A Feedback Loop Built on User Behavior
This process of tracking, analyzing, and adjusting based on user actions creates a feedback loop. Each query, each click, provides new insights into what users find helpful. This feedback loop enhances search quality, making results more relevant and reliable.
Take the example of flu season. When users search for “flu symptoms” during this time, Google may notice a trend in which results users click and where they spend time on the page. If users consistently click links that offer straightforward symptom lists rather than dense medical studies, Google may prioritize results that provide easy-to-understand information.
Continuous Learning for Better Results
Through this constant learning from clicks and signals, Google stays in tune with changing needs and preferences. While the process may appear seamless, it’s driven by millions of user interactions, all contributing to a more accurate search experience.
In short, Google’s use of click data and interaction signals makes its search engine dynamic, responsive, and fine-tuned to deliver relevant results. What seems like a simple list of links is the result of countless data points and insights gathered from user actions, making Google search feel intuitive and helpful for everyone.
Measuring UX Through SEO Metrics
To understand how UX affects SEO, track specific metrics that Google uses to evaluate user experience:
- Click-Through Rate (CTR)
This metric measures how often users click on a link in search results. A high CTR indicates that the page is appealing and relevant, which can improve its rank. - Bounce Rate
Bounce rate shows the percentage of visitors who leave a page without interacting further. A high bounce rate can signal that the content doesn’t meet user expectations, while a low bounce rate often indicates relevance and quality. - Time on Page
This metric reflects how long users spend on a page, showing how engaged they are with the content. Longer time on page suggests the content is meeting user needs. - Pages per Session
This metric tracks how many pages a user visits in one session. Higher pages per session indicate that navigation is effective and that users find the content valuable. - Scroll Depth and Interaction
Google also considers how users interact with page elements, such as scrolling depth and clicks on images or dropdowns. High engagement levels signal that users find the content engaging and useful, which supports higher rankings.
How to Build a UX-SEO Strategy
A successful UX-SEO strategy focuses on areas that improve both user engagement and search performance. Here are some steps to get started:
- Audit Your Site for UX and SEO Issues
Start by analyzing your site’s current performance, page speed, mobile compatibility, and navigation. Tools like Google PageSpeed Insights and Core Web Vitals can identify areas to improve, such as slow-loading pages or mobile usability issues. - Prioritize Page Speed
Improving page speed directly boosts user satisfaction and rankings. Compress images, reduce heavy scripts, and enable lazy loading for content that’s not immediately visible. - Enhance Mobile Responsiveness
A mobile-friendly site keeps users engaged and improves rankings. Test for mobile compatibility, ensuring that buttons and links are easy to tap, and that the layout adjusts seamlessly to different screen sizes. - Focus on Content Quality
Content that addresses user questions clearly and concisely can increase engagement and reduce bounce rates. Use headings, bullet points, and multimedia elements to keep users interested. - Improve Site Navigation
Simple, logical navigation makes it easier for users to find what they need. Organize menus clearly, guide users with calls to action, and limit page depth to keep content accessible. - Regularly Monitor User Engagement
Track key metrics like CTR, bounce rate, and time on page to see how users are engaging with your site. Heatmaps and A/B testing can also help you identify areas for improvement and refine the user experience.
Why UX Matters for SEO Success
Ignoring UX can seriously impact SEO and hold back your website’s potential. Here’s what can happen if UX is left out of your SEO efforts:
- Higher Bounce Rates
Poor UX can drive users away, whether due to slow load times, hard-to-use navigation, or irrelevant content. High bounce rates signal low value to Google, which can lower your rankings. - Lost Conversions
If users can’t easily find what they’re looking for, they’re less likely to take action, whether that’s making a purchase, signing up, or reading more. Poor UX can cost you conversions, impacting revenue. - Reduced Search Visibility
Google ranks pages based on quality, relevance, and engagement. A site with poor UX may struggle to rank well, losing visibility and traffic to competitors with stronger user experiences. - Missed Revenue Opportunities
Sites with high rankings and positive user experiences gain more visibility, traffic, and conversions. Failing to focus on UX and SEO could mean lost revenue as competitors capture those visitors.
Examples of Great User Experience and SEO
Here are three websites that do a great job blending strong User Experience (UX) with effective Search Engine Optimization (SEO):
ASOS employs clear navigation and descriptive URLs, enhancing both user experience and search engine indexing.
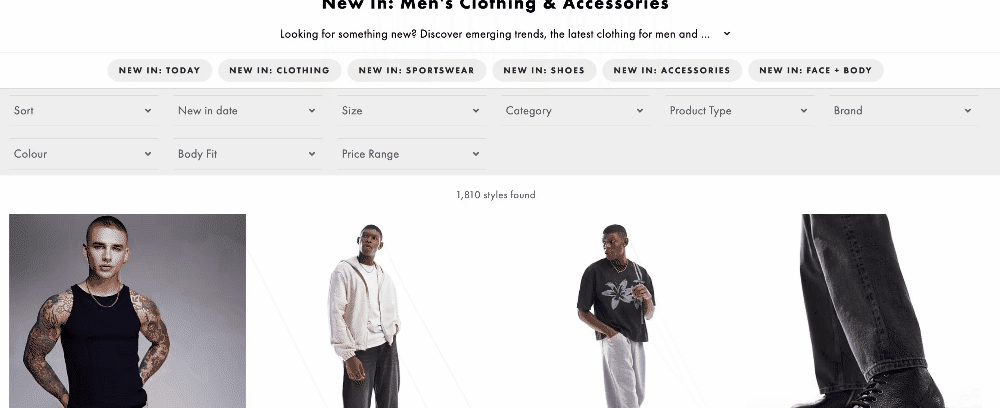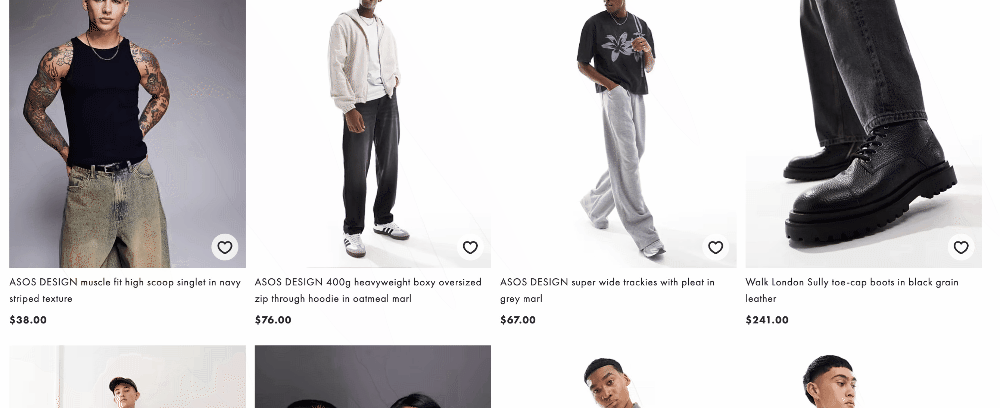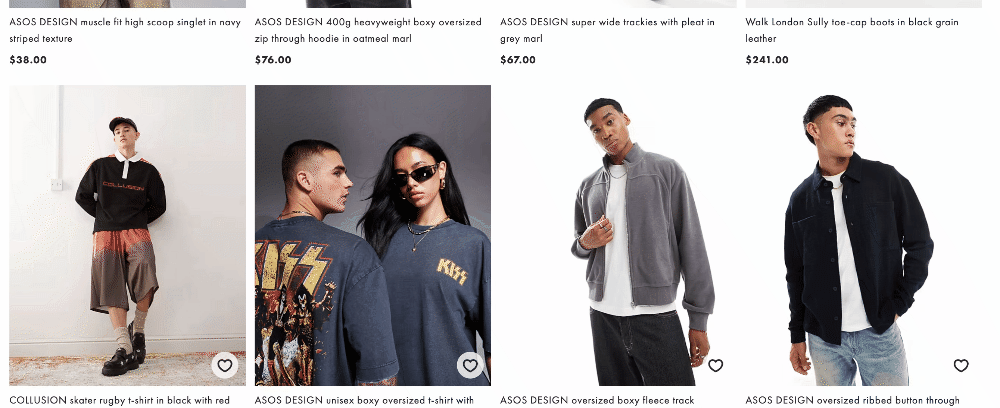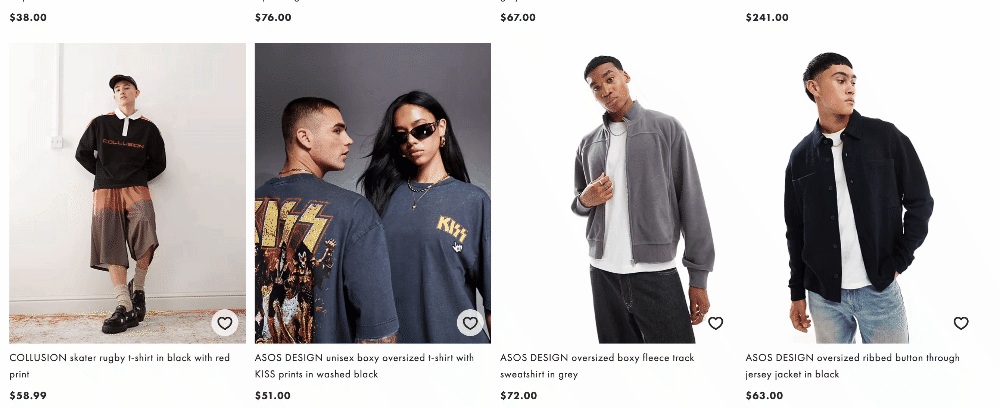
Amazon features user-generated content, such as reviews and ratings, which enriches the site’s content and improves search visibility.
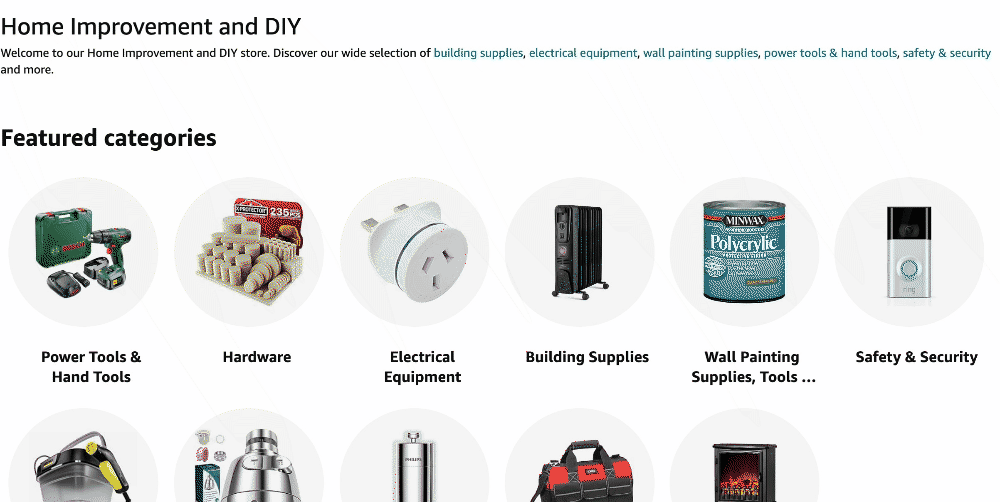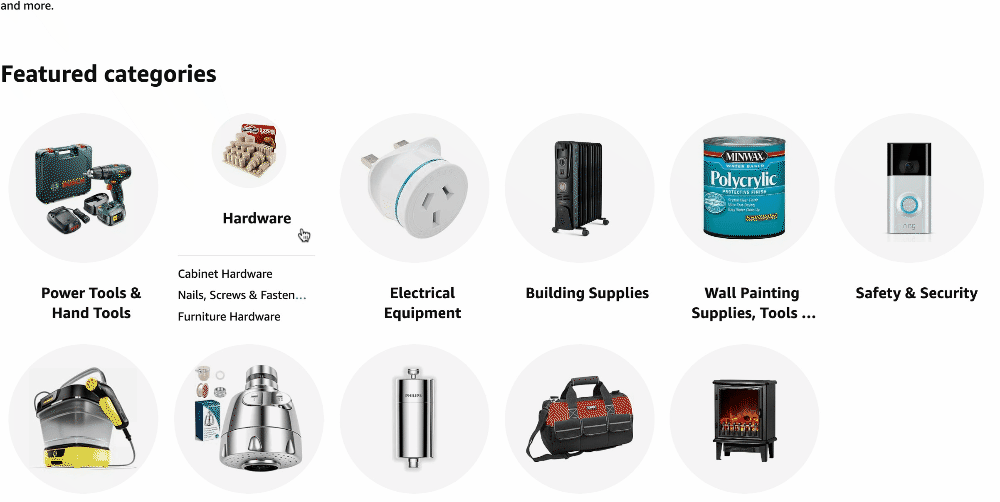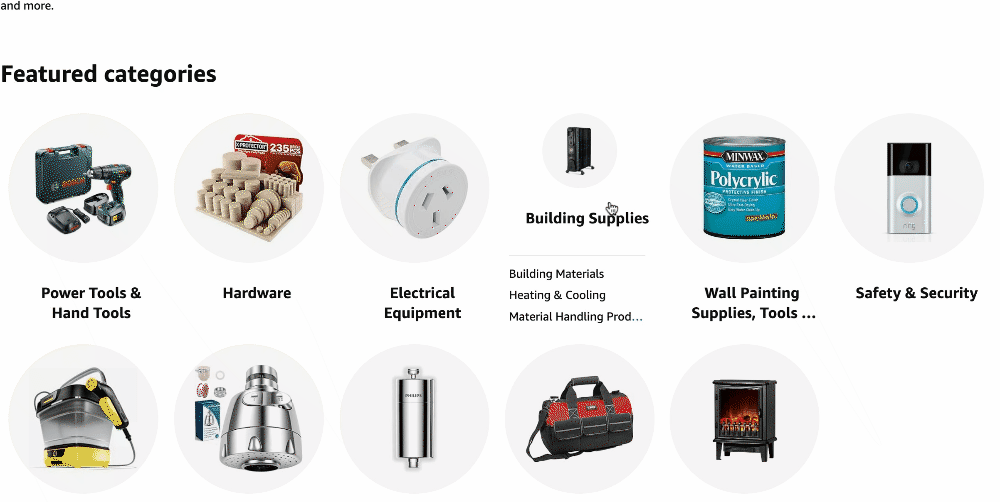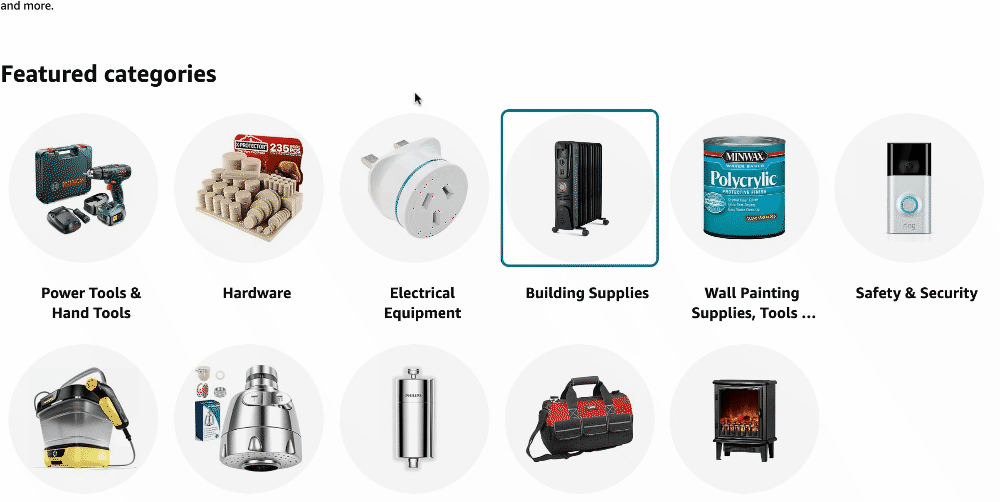
Zappos stands out for its thoughtful UX design. Breadcrumb navigation makes it easy to move from one category to another, turning online shopping into a straightforward, enjoyable experience.

These examples show how smart design can make sites both enjoyable for users and friendly for search engines. By focusing on simplicity, intuitive layouts, and clear navigation, these brands deliver a browsing experience that satisfies users and meets SEO goals.
Ready to Optimize Your Website’s UX & SEO?
Remember, the goal is to create a website that ranks well and provides real value to your visitors. Focus on creating experiences that serve both your users and search engines, and you’ll be on your way to digital success.
- Do a full UX-SEO audit
- Prioritize changes based on impact and effort
- Make changes systematically
- Measure and adjust
The intersection of UX and SEO is one of the biggest opportunities in digital marketing today. By focusing on bot, you’re not optimizing for search engines or users – you’re creating a website that succeeds everywhere.