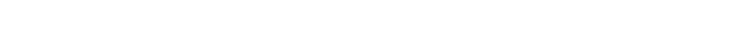What Are Semantically Related Keywords?
For example, consider the keyword “organic gardening”.
Semantically related keywords could include:
- “Compost tips”
- “Natural pest control”
- “Heirloom seeds”
These terms are distinct but share a clear connection to the practices and principles of organic gardening.
Another example – for the keyword “smartphone photography”, semantically related keywords might be:
- “Mobile editing apps”
- “Phone camera accessories”
- “Social media photo sharing”
While varied, they all tie back to the central theme of taking and sharing photos with a smartphone.
What is Semantic Search?
In semantic search, search engines like Google aren’t just looking for exact word matches in your query.
They try to grasp the underlying intent and broader context of your search. It’s like they’re putting the puzzle pieces of your query together to find the best possible answers.
This approach is especially useful when your search terms are broad or open to interpretation.
Additionally, Google is a semantic search engine, meaning it tries to understand the content’s meaning rather than just keyword matches.
Google uses Natural Language Processing (NLP) algorithms to understand content.
This advanced technology helps Google delve into the meaning of words and phrases, enhancing its ability to match search queries with relevant content that truly addresses the user’s intent.
Semantics in SEO is about linking words and phrases based on their deeper, interconnected meanings. This not only helps search engines provide more tailored results but also guides websites to create pieces of content or blog posts that align closely with what people are searching for.
Understanding these connections between words can significantly enhance the search experience for users.
For SEO experts, by focusing on the meaning and context of content rather than just keywords, you can create more impactful and relevant content that resonates both with search engines and your audience.
How semantic keywords have evolved
SEO, or Search Engine Optimization, has really changed over time.
A big moment in this evolution was in 2013 with Google’s Hummingbird update. This wasn’t just a small tweak but a complete overhaul of Google’s core algorithm.
How Hummingbird, RankBrain, and BERT Improved Search
Semantic search has changed how search engines handle information. Key updates like Hummingbird, RankBrain, and BERT contributed to this shift, each advancing how well search engines interpret queries.
Hummingbird (2013)
Hummingbird was a major improvement in understanding what users want instead of just matching specific words.
This update focused on interpreting queries with natural language processing, giving more relevant answers by looking beyond exact keywords. Hummingbird recognized context, providing search results that better reflected the user’s intent.
RankBrain (2015)
RankBrain introduced machine learning to search algorithms, allowing search engines to analyze query patterns and better grasp intent.
This meant that even if a query didn’t contain exact keywords, RankBrain could understand related terms and deliver suitable results. Users could find accurate information through a wider range of similar phrases.
BERT (2019)
BERT improved on understanding language subtleties, especially in longer, conversational queries. It focused on prepositions and context within sentences, which helped search engines interpret the meaning more accurately.
With BERT, searches could capture the nuances of natural language, leading to results that more precisely matched what users intended.
Together, these updates shifted search from a focus on keywords to a better understanding of human language.
Users now receive information that aligns more closely with what they’re genuinely looking to find.
Why Entities and Relationships Matter in Semantic Search
In semantic search, entities and relationships play key roles in helping search engines accurately interpret and rank content.
Entities: Defining Core Concepts
Entities are distinct, recognizable terms, such as people, places, or objects that represent unique ideas. For instance, “carbon dioxide” is an entity that carries a specific meaning understood globally. Entities like these serve as core concepts in content, giving it clear, identifiable terms that search engines can recognize and associate with relevant searches.
Relationships: Building Context and Connections
Relationships define how entities relate to each other, adding layers of context. For example, the relationship between “carbon dioxide” and “greenhouse gases” highlights an important connection. These links between entities give search engines a clearer picture of your content’s broader context, which helps in presenting the content more accurately in search results.
Enhancing Search Relevance
Using semantically related keywords through entities and relationships aligns your content with how search engines interpret queries. This approach not only improves ranking potential but also helps content reach a more specific audience actively searching for information on these topics. By focusing on relevant entities and their relationships, your content can achieve greater visibility and meet user intent effectively.
What is Google’s Goal with Semantic Search?
To make searches faster and more precise. The cool part about Hummingbird was how it shifted the focus from just counting how many times a keyword appeared (keyword frequency) to understanding the meaning behind searches (semantic relevance) that links between.
Before Hummingbird, Google would look at a webpage and try to find all the words that matched a search query exactly. It was like a word-for-word match game.
But after Hummingbird, things changed through algorithm updates.
Google started to focus more effort on what your search actually means, not just the words you use. It became smarter at figuring out which words in your search were really important and which weren’t. This was a big deal for natural language queries, where not every word might be crucial to understanding what you’re looking for.
This update also made context and related terms in content more important. Now, it wasn’t enough for content creators to just stuff their articles with specific keywords. They had to make sure their content was relevant to the context and included terms related to the main keywords. This pushed SEO towards a more user-centric approach. It became more about understanding and meeting what the user is really looking for, rather than just trying to game the system with lots of keywords.
The introduction of semantic relevance in SEO with Google’s Hummingbird update marked a shift towards creating meaningful content that really addresses what people are searching for. It’s all about understanding the user’s intent and delivering the right content, which is key for higher search rankings. That’s where semantic search is playing a key role in SEO.
How semantic keywords changed SEO
The rise of semantic keywords has indeed transformed SEO, but it hasn’t necessarily made it more difficult. It’s more about a shift in focus.
In the past days of SEO was a lot about picking a target keyword and repeating it in the title, headers, body text, and so on. It was like having a magic word that you used everywhere to get noticed by search engines.
But now, things have evolved. Google’s search engine has become much smarter at understanding what users are really looking for—their intent.
So, the strategy has changed. Instead of just focusing on a single keyword phrase, it’s about exploring the whole landscape around that phrase with a semantic search.
You choose a target phrase, sure, but you also dive into phrases that are semantically related to it.
Your content should answer a range of questions that are connected to the broader topic. This way, you’re not just optimizing for that one keyword phrase; you’re covering a wider area – that’s a semantic relationship.
What this means is that your content becomes more comprehensive, addressing various aspects of the topic.
This can help your page rank not only for your primary keyword phrase but also for those semantically related keywords. It’s like casting a wider net to catch more fish – in this case, a broader range of search queries.
The shift to semantic keywords doesn’t make SEO harder, but it does make it more holistic.
It’s about optimizing for a topic, not just a keyword phrase, which can lead to richer and more comprehensive content and potentially better search engine performance.
How can you find semantic keywords?
Using tools, you can find these semantically related words and secondary keywords, and using that list, you can formulate a great user experience that avoids keyword stuffing and has the right keyword density.
Using Google’s Related Search Suggestions And Search Results
Google’s related search suggestions and search results are a goldmine for finding semantic keywords. When you type a keyword into Google’s search bar, it lists related search suggestions. These suggestions are based on what other people are searching for, making them a valuable resource for semantic keywords.
Additionally, the search results for a keyword can also provide semantic keywords. The content of the top-ranking pages of relevant search results often contains words and phrases that are semantically related to the keyword. It’s like fishing in a well-stocked pond—you’ll likely catch something valuable for semantic search and a beneficial keyword cluster.
Utilizing Google Ads Tool For Keyword Planning
Google Ads Keyword Planner is another keyword research tool for finding semantic keywords. It provides insights into the search volume and competition for various keywords and suggests related ones.
This tool can help you identify semantic keywords with a high search volume but low competition, which can benefit your SEO strategy. It’s like having a map that guides you to the most fruitful semantic keyword research and harvesting areas.
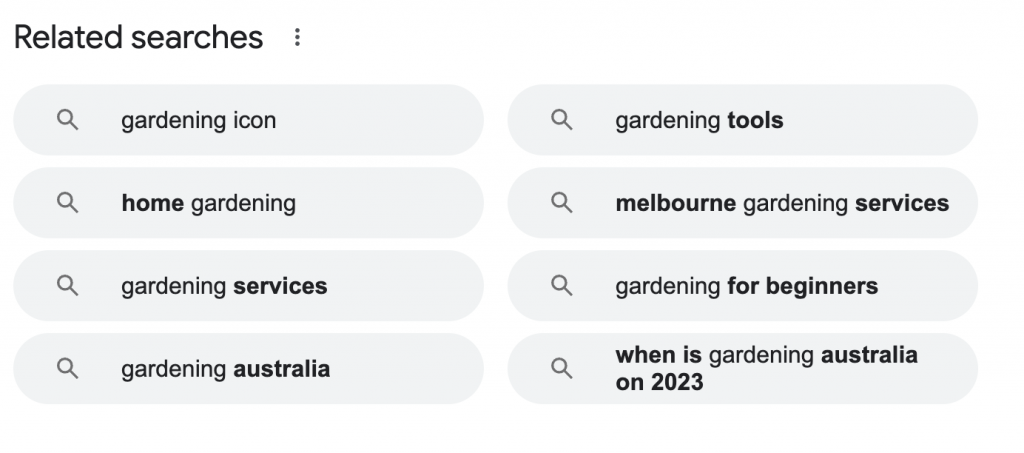
Exploring Google Trends For Related Searches And Topics
Google Trends is a powerful tool for identifying trending topics and related searches. By entering a keyword into Google Trends, you can see how its popularity has changed and what related topics and queries are trending. This can help you identify semantic keywords that are currently popular, allowing you to capitalize on current trends. It’s like surfing the wave of widespread interest, using it to propel your content to greater visibility.
Monitoring Social Media Conversations For Real-Time Trends
With its rapidly growing user base and dynamic content, TikTok is an excellent platform for identifying real-time trends and semantic keywords for online marketing. Here’s an example of how you could use it:
Let’s say your main keyword is “sustainable fashion.” You could start by searching for this term on TikTok and observing the popular videos and their associated hashtags.
You might find related hashtags like #EcoFriendlyClothing, #UpcycledFashion, or #ThriftFlips. These are all semantic keywords related to your main target keyword.
Furthermore, you can watch the videos and listen to the language creators and users use in the comments. You might come across phrases like “zero waste outfits,” “ethical fashion brands,” or “DIY clothing hacks.”
These phrases are also semantic keywords that people are currently using and engaging with on the topic of sustainable fashion.
In this way, TikTok serves as a live, global conversation you can tap into for fresh ideas and relevant semantic keywords. It’s like being at a large party, listening to the buzz of conversation, and picking up on the popular topics and phrases of the moment for semantic search.
Using SEMrush’s Keyword Magic Tool For Comprehensive Keyword Information
SEMrush’s Keyword Manager Tool is a comprehensive resource for keyword research. It provides detailed information about keywords, including their search volume, keyword difficulty, and more. It also suggests related keywords, secondary keywords, making it a valuable tool for finding semantic keywords.
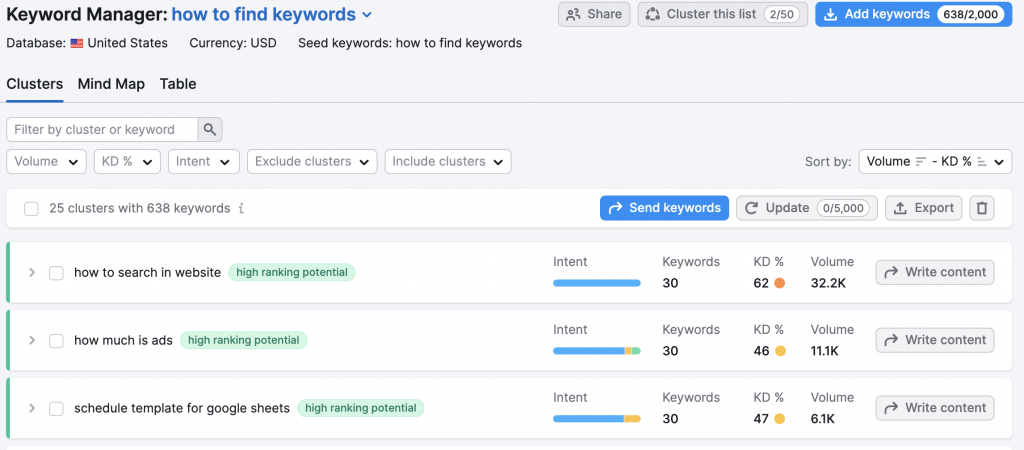
Using this tool is like having a personal guide who knows the terrain of keyword research inside out and can lead you to the most valuable finds and create an amazing list of keywords.
Remember, finding semantic keywords is like a treasure hunt. The more diverse your source’s target keywords are, the more likely you find valuable keywords that can enhance your content that nail search intent.
Applying Semantic Keywords In SEO Strategy
Semantic keywords can be thought of as the threads that weave together the fabric of your content, providing depth and richness.
Incorporating a semantic core keyword into your content creation process is crucial for enhancing the relevance and comprehensiveness of your content.
When writing, consider the various aspects of your topic and the related terms that could be used to discuss these aspects. Incorporate these semantic keywords naturally into your content, ensuring that they enhance the readability and value of your content rather than disrupting it.
This approach can help you create content that is engaging for your audience and highly relevant for search engines.
Monitoring Semantic Keyword Metrics
Monitoring keyword metrics such as search volume is akin to keeping a finger on the pulse of your SEO strategy. It’s a good step after your keyword research.
It allows you to understand which semantic keyword is attracting attention and which might need to be adjusted. High-volume search keywords can drive traffic but can also be highly competitive. Balancing high and low-volume semantic keywords can help you tap into broad and niche markets.
Semantic keywords also play a crucial role in content ranking. They help search engines understand the context of your content, improving its relevance and, thus, its ranking. It’s like providing a detailed map to a treasure hunter—the more information you provide, the more likely they will find it. In this case, the prize is your content, and the hunter is the search engine. Using semantic keywords effectively can guide search engines to your content, improving its visibility and ranking.
Why do I have to include semantically related keywords in my content?
When your webpages have a variety of semantically related keywords, they offer a more complete picture of the subject. This isn’t just about throwing in a bunch of related words; it’s about building a comprehensive background that enriches your content.
From Google’s perspective, when it sees semantically related keywords, it can better understand the connections between different topics your content covers. It’s like giving Google a map that shows not just the main destination (your primary keyword) but also the interesting landmarks (related keywords) around it. This helps Google see how your content answers not just one specific query but a range of related questions.
Having semantically related keywords means your content isn’t just narrowly focused on one thing. Instead, it’s like a well-rounded guide on a topic, making it more likely to perform well in search results. Google gets a clearer picture of what your page is about, and users get more comprehensive answers to their queries. It’s a win-win for both search engines and searchers!
What are semantic keywords examples?
Here are a couple of examples:
- Primary Keyword: “Digital Marketing”
- Semantic Keywords:
- “online advertising,” “social media strategy,” “content marketing,” “SEO techniques,” “email campaigns.”
- Primary Keyword: “Healthy Eating”
- Semantic Keywords:
- “nutritious recipes,” “balanced diet,” “organic foods,” “meal planning tips,” “vitamins and supplements.”
In each of these cases, the semantic keywords are not just synonyms of the primary keyword but are related concepts that help to flesh out the topic. By including these in your content, you provide a richer, more comprehensive exploration of the subject, which is beneficial for SEO and user engagement.